Latest 2025 Updated United States Medical Licensing Exam Step 1 Questions and Answers
USMLE Question Bank & Practice Tests
Practice Tests with official USMLE Exam Questions - Updated on Daily Basis
100% Pass Guarantee


USMLE PDF Questions : Download 100% Free USMLE Exam Questions
Exam Number : USMLE
Exam Name : United States Medical Licensing Exam Step 1
Vendor Name : USMLE
Update : Click Here to Check Latest Update
Question Bank : Check Questions
Real Test USMLE Exam Questions
Seeking authentic USMLE test prep questions Practice Test with valid questions for the USMLE United States Medical Licensing Exam Step 1 Exam? Killexams.com offers recently updated and genuine USMLE PDF Download Practice Test sourced from actual USMLE exams. Simply study our comprehensive materials and confidently take the exam to achieve success.
Providing merely Pass Guides is definitely not enough. Reviewing unnecessary material for USMLE does not help. This just makes you more confused regarding USMLE topics until you acquire reliable, appropriate, and up-to-date USMLE TestPrep questions and a VCE practice test. Killexams.com is the leading provider of quality USMLE TestPrep material, legitimate Questions and Answers, fully tested boot camp, and VCE Practice Tests. All of this is merely a few clicks away. Just visit killexams.com to download your completely free copy of USMLE TestPrep PDF. Read the sample questions and endeavor to understand them. When you are satisfied, sign up for your full copy of USMLE boot camp. You will obtain your username and a password, which you will use on the website to log on to your download account. You will then see USMLE certification test prep files, prepared to download, and VCE practice test files. Download and Install the USMLE VCE practice test software and load the test for practice. You will see just how significantly your knowledge is improved. This will make you so self-confident that you will decide to sit in the actual USMLE examination within 24 hours.
You should never compromise on the USMLE certification test prep top quality if you need to save your time and money. Do not ever turn to free USMLE TestPrep provided online because there is no guarantee regarding that stuff. Many individuals continue to submit outdated material online all the time. Directly visit killexams.com and get 100% Free USMLE PDF before you acquire the full version of USMLE questions bank. This will save you from big hassle. Simply memorize and practice USMLE TestPrep before you ultimately face a real USMLE examination. You will secure a good score throughout the exact test.
We present Actual USMLE test Issues and Answers boot camp in two formats: USMLE PDF report and USMLE VCE test simulator. USMLE Real evaluation is rapidly modified by USMLE in the authentic tests. The USMLE certification test prep PDF document may be downloaded on any device. You can create publications from USMLE TestPrep to make your very own study material. Our pass rate is high, up to 98.9%, and moreover, the identicalness of our USMLE questions with the real test is 98%. Do you need success in the USMLE test in just one endeavor? Right away go to download USMLE USMLE real test questions at killexams.com.
Key Features of Killexams USMLE TestPrep:
- USMLE TestPrep Download Access in just 5 min.
- Complete USMLE Questions Bank
- USMLE Exam Success Guarantee
- Guaranteed Actual USMLE exam questions
- Latest and 2025 updated USMLE Questions and Answers
- Latest 2025 USMLE Syllabus
- Download USMLE Exam Files anywhere
- Unlimited USMLE VCE Exam Simulator Access
- No Limit on USMLE Exam Download
- Great Discount Coupons
- 100% Secure Purchase
- 100% Confidentiality Ensured
- 100% Free Pass Guides Sample Questions
- No Hidden Cost
- No Monthly Subscription
- No Auto Renewal
- USMLE Exam Update Intimation by Email
- Free Technical Support
Exam Details: https://killexams.com/pass4sure/exam-detail/USMLE
Pricing Information: https://killexams.com/exam-price-comparison/USMLE
See Complete List: https://killexams.com/vendors-exam-list
Discount Coupon on Full USMLE certification test prep questions:
- WC2020: 60% Flat Discount on each exam
- PROF17: 10% Further Discount on Value Greater than $69
- DEAL17: 15% Further Discount on Value Greater than $99
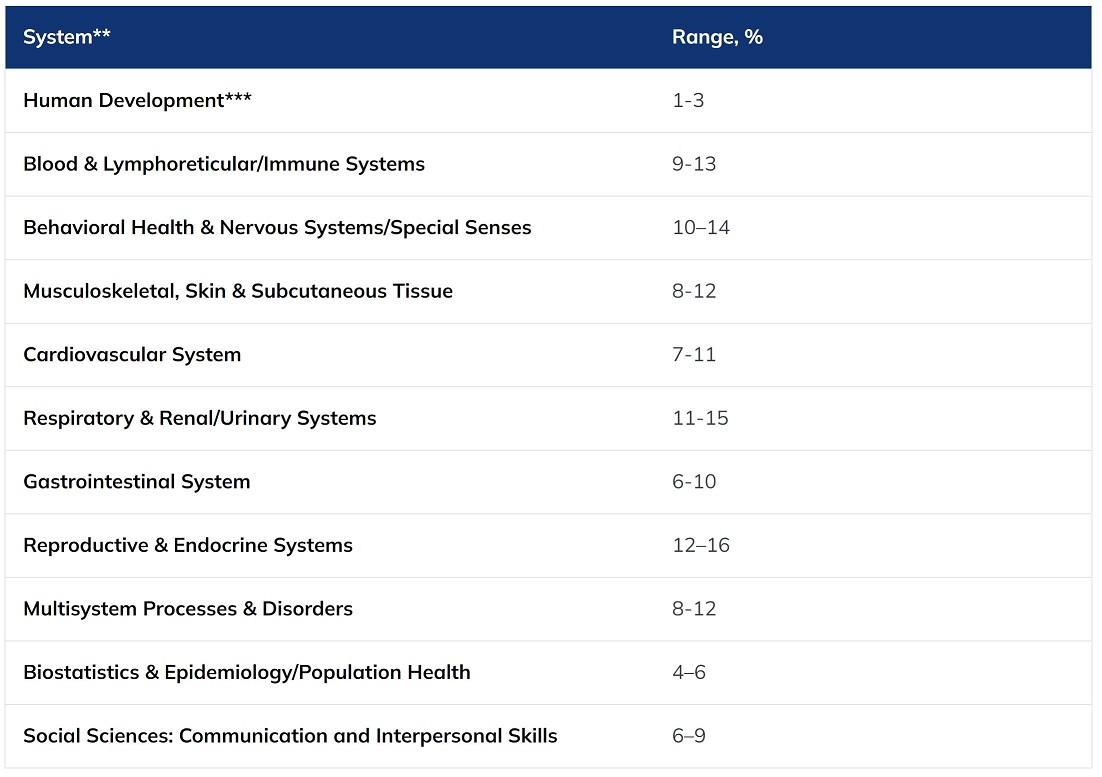
Beginning in May 2020, Step 1 examinations will include an increased number of questions that assess communications skills. The tables below provide information on the content weighting for Step 1 examinations administered before and after May 2020.
Table of Contents
- General Principles of Foundational Science
- Immune System
- Blood & Lymphoreticular System
- Behavioral Health
- Nervous System & Special Senses
- Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue
- Musculoskeletal System
- Cardiovascular System
- Respiratory System
- Gastrointestinal System
- Renal & Urinary System
- Pregnancy, Childbirth, & the Puerperium
- Female Reproductive System & Breast
- Male Reproductive System
- Endocrine System
- Multisystem Processes & Disorders
- Biostatistics, Epidemiology/Population Health
- Interpretation of the Medical Literature
- Social Sciences
Biochemistry and molecular biology
Gene expression: DNA structure, replication, exchange, and epigenetics (eg, imprinting, Xactivation, DNA methylation)
Gene expression: transcription
Gene expression: translation, post-translational processing, modifications, and disposition of
proteins (degradation), including protein/glycoprotein synthesis, intra-extracellular
sorting, and processes/functions related to Golgi complex and rough endoplasmic
reticulum
Structure and function of proteins and enzymes (eg, enzyme kinetics and
structural/regulatory proteins)
Energy metabolism (eg, ATP generation, transport chain)
Biology of cells
Adaptive cell responses and cellular homeostasis (eg, hypertrophy)
Mechanisms of injury and necrosis, including pathologic processes (eg, liquefactive necrosis,
free radical formation)
Apoptosis
Cell cycle and cell cycle regulation (eg, mitosis)
Mechanisms of dysregulation
cell biology of cancer (eg, role of p53, proto-oncogenes)
general principles of invasion and metastasis, including cancer staging
Cell/tissue structure, regulation, and function, including cytoskeleton, organelles,
glycolipids, channels, gap junctions, extracellular matrix, and receptors
Human development and genetics
Principles of pedigree analysis
inheritance patterns
occurrence and recurrence risk determination
Population genetics: Hardy-Weinberg law, founder effects, mutation-selection equilibrium
Principles of gene therapy
Genetic testing and counseling
Genetic mechanisms (eg, penetrance, genetic heterogeneity)
Biology of tissue response to disease
Acute inflammatory responses (patterns of response)
acute inflammation and mediator systems (eg, histamine, prostaglandins, bradykinins,
eosinophilic basic protein, nitric oxide)
vascular response to injury, including mediators
principles of cell adherence and migration (eg, ECAMs, selectins, leukocytic
diapedesis, and rolling)
microbicidal mechanisms and tissue injury (eg, defensins)
clinical manifestations (eg, pain, fever, leukocytosis, leukemoid reaction, chills)
Chronic inflammatory responses (eg, tumor necrosis factor)
Reparative processes
wound healing, repair: thrombosis, granulation tissue, angiogenesis, fibrosis,
scar/keloid formation
regenerative process
Pharmacodynamic and pharmacokinetic processes: general principles
Pharmacokinetics: absorption, distribution, metabolism, excretion, dosage intervals
Mechanisms of drug action, structure-activity relationships (eg, anticancer drugs)
Concentration and dose-effect relationships (eg, efficacy, potency), types of agonists (eg,
full, partial, inverse) and antagonists and their actions
Individual factors altering pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics (eg, age, gender,
disease, tolerance, compliance, body weight, metabolic proficiency,
pharmacogenetics)
Mechanisms of drug adverse effects, overdosage, toxicology
Mechanisms of drug interactions
Signal transduction, including structure/function of all components of signal transduction
pathways such as receptors, ligands (eg, general principles of nitric oxide, autocrine
and paracrine signaling)
Microbial biology
Microbial identification and classification, including principles, microorganism
identification, and non-immunologic laboratory diagnosis
Bacteria
structure (eg, cell walls, composition, appendages, virulence factors, extracellular
products, toxins, mechanism of action of toxins)
processes, replication, and genetics (eg, metabolism, growth, and regulation)
oncogenesis
antibacterial agents (eg, mechanisms of action on organism, toxicity to humans, and
mechanisms of resistance)
Viruses
structure (eg, physical and chemical properties, virulence factors)
processes, replication, and genetics (eg, life cycles, location of virus in latent infection)
oncogenesis
antiviral agents (eg, mechanisms of action on virus, toxicity to humans, and
mechanisms of resistance)
Fungi
structure (eg, cell wall, composition, appendages, virulence factors, extracellular
products, toxins, mechanisms of action of toxins)
processes, replication, and genetics (eg, asexual vs. sexual, metabolism, growth)
antifungal agents (eg, mechanisms of action on fungus, toxicity to humans, and
mechanisms of resistance)
Parasites
structure (eg, appendages, macroscopic features, and virulence factors)
processes, replication, and genetics (eg, life cycles, metabolism, and growth)
oncogenesis
antiparasitic agents (eg, mechanisms of action on parasite, toxicity to humans, and
mechanisms of resistance)
Prions
Normal age-related findings and care of the well patient
Infancy and childhood (0-12 years)
Normal physical changes: linear growth, variations in linear growth, including
constitutional delay; weight; head circumference; micturition, defecation,primary
incontinence/bedwetting; normal physical examination; screening; sleep;
teething syndrome
Developmental stages: motor; speech; cognitive; psychosocial; anticipatory guidance
Lifestyle and routine preventive health care: nutrition; exercise (eg, benefits of
exercise); preventive/travel medicine; risk factors and prevention (eg, guns,
swimming, motor vehicles, car seats); routine vaccinations
Adolescence (13-17 years)
Normal physical changes: linear growth, variations in linear growth including
constitutional delay; weight; puberty; normal physical examination; gynecomastia;
autonomy/self-identity; sleep
Developmental stages: cognitive (eg, abstract thought); psychosocial (eg, autonomy, role
confusion, sexual identity); anticipatory guidance
Lifestyle and routine preventive health care: nutrition; exercise (eg, benefits of
exercise); preventive/travel medicine; risk factors and prevention (eg, risk-taking
behavior, helmets, safe sex, motor vehicles, seat belts, distractions); routine
vaccinations
Adulthood (18-64 years)
Normal physical changes: weight; normal physical examination; screening; sleep
Developmental stages: cognitive; intimacy vs isolation; anticipatory guidance
Lifestyle and routine preventive health care: nutrition; exercise (eg, benefits of
exercise); preventive/travel medicine; risk factors and prevention; routine
vaccinations
Senescence (65 years and older)
Normal physical changes, including normal physical exam for age: weight, height
(spinal compression), skin, bruising; normal physical examination; response to
temperature; micturition, defecation;sleep
Developmental stages: motor; cognitive (eg, benign senescent forgetfulness);
psychosocial; integrity vs despair; retrospection; anticipatory guidance
Lifestyle and routine preventive health care: nutrition; exercise (eg, benefits of exercise);
preventive/travel medicine; risk factors and prevention (eg, falls, general medical
condition; polypharmacy, driving, caregiver stress); routine vaccinations
Immune System
Normal processes
Development of cells of the adaptive immune response, including positive and
negative selection during immune development
Structure, production, and function
granulocytes, natural killer cells, macrophages, mast cells, dendritic cells, cell receptors
(eg, complement receptors and toll-like receptors), cytokines, chemokines
T lymphocytes, including T-lymphocyte receptors, accessory molecules (eg, CD3, CD4,
CD8, B7), cell activation and proliferation, cytotoxic T lymphocytes, and memory T
lymphocytes
B lymphocytes and plasma cells, including B-lymphocyte receptors, immunoglobulins, cell
activation and proliferation, including development of antibodies and memory B
lymphocytes
host defense mechanisms, host barriers to infection, mucosal immunity (eg, gutassociated lymphoid tissue and bronchus-associated lymphoid tissue),
anatomical locations of T and B lymphocytes
Cellular basis of the immune response and immunologic mediators
antigen processing and presentation in the context of MHC I and MHC II molecules (eg,
TAP, beta-2 microglobulin), intracellular pathways, mechanisms by which MHC is
expressed on the surface; including distribution of MHC I and MHC II on different
cells, mechanisms of MHC I and MHC II deficiencies, and the genetics of MHC
regulation of the adaptive immune response (eg, peripheral tolerance, anergy,
regulatory T lymphocytes, termination of immune response, and B-T
lymphocyte interactions)
activation, function, and molecular biology of complement (eg, anaphylatoxins)
functional and molecular biology of cytokines (eg, IL 1-15)
Basis of immunologic diagnostics (eg, antigen-antibody reactions used for diagnostic
purposes, ELISA, immunoblotting, antigen-antibody changes over time, ABO
typing)
Principles of immunologic protection
vaccine production and mechanisms of vaccine action
biologically active antibodies (eg, monoclonal antibodies, polyclonal antibodies
including IVIG, VZIG, rabies immunoglobulin)
Effect of age on the function of components of the immune system
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Disorders associated with immunodeficiency
deficiency primarily of humoral immunity: common variable immunodeficiency;
hyper IgM syndrome; hypogammaglobulinemia/agammaglobulinemia, X-linked
(Bruton); selective immunodeficiency (eg, IgA, IgM, IgE)
deficiency/dysfunction primarily of cell-mediated immunity: adenosine deaminase
deficiency; DiGeorge syndrome; severe combined immunodeficiency disease
(SCID); Wiskott-Aldrich syndrome; granulomatosis; allergic reactions/skin
complement deficiency: alternative pathway component deficiency (C2, C3b, C3bB,
C36B6); classical pathway component deficiency (C1q, C1r, C1-C5); terminal
component deficiency (C5b-C9; terminal complement complex); C1 esterase
inhibitor deficiency, hereditary angioedema; mannose-binding lectin (MBL)
deficiency; membrane attack complex deficiency
deficiency of phagocytic cells and natural killer cells: Chediak-Higashi disease; chronic
granulomatous disease and other disorders of phagocytosis; leukocyte adhesion
deficiency
HIV/AIDS: HIV1 and HIV2; AIDS; AIDS complications (eg, neuropathy, dementia, renal
insufficiency); immunology of AIDS; immune reconstitution syndrome (IRS);
secondary infections; noninfectious complications
Immunologically mediated disorders
hypersensitivity reactions: type 1, 2, 3, including anaphylaxis; type 4; drug reactions;
serum sickness
transplantation: rejection; graft-vs-host disease
Adverse effects of drugs on the immune system: Jarisch-Herxheimer reaction; drugs
affecting the immune system (eg, prednisone, azathioprine, cyclosporine,
methotrexate, monoclonal antibody drugs [eg, abciximab, adalimumab; bevacizumab,
infliximab, omalizumab, rituximab]); vaccine adverse effects
Blood & Lymphoreticular System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
Organ structure and function
Cell/tissue structure and function
production and function of erythrocytes, including heme and hemoglobin synthesis;
hemoglobin O2 and CO2 transport, transport proteins, erythropoietin
production and function of platelets
production and function of coagulation and fibrinolytic factors; hemostasis
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious and immunologic
infectious disorders
bacteria
viral: hemorrhagic fever (Ebola virus, Marburg virus); chikungunya; dengue fever;
Zika virus disease
parasitic: malaria (Plasmodium spp); babesiosis (Babesia species)
primary infections of lymphoid tissue: lymphadenitis (viral, bacterial, fungal,
parasitic); lymphangitis; buboes, bubonic plague (Yersinia pestis); cat scratch
disease (Bartonella henselae)
immunologic and inflammatory disorders: cryoglobinemia, essential mixed
cryoglobinemia; autoimmune hemolytic anemia; paroxysmal nocturnal
hemoglobinuria; thrombotic thrombocytopenic purpura; hemolytic uremic
syndrome
Neoplasms: leukemia, acute (ALL, AML); leukemia, chronic (CLL, CML); lymphomas, Hodgkin
disease, non-Hodgkin lymphoma, Burkitt lymphoma, T-cell lymphoma; multiple myeloma,
dysproteinemias, monoclonal gammopathy of unknown significance (MGUS);
myelofibrosis; myelodysplastic syndrome, myelodysplasias; other immunoproliferative
neoplasms (eg, Waldenstrom macroglobulinemia)
Anemia, cytopenias, and polycythemia anemias
decreased production: anemia of chronic disease
hemolysis: glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency; pyruvate kinase deficiency
disorders of hemoglobin, heme, or membrane: disorders of red cell membranes;
hereditary spherocytosis, elliptocytosis; methemoglobinemia, congenital; sickle
cell disease; sideroblastic anemia; thalassemias
other causes of anemia: blood loss, acute and chronic as a cause of anemia
cytopenias: aplastic anemia; leukopenia; neutropenia, cyclic neutropenia,
agranulocytosis; pancytopenia; thrombocytopenia, quantitative; immune
thrombocytopenic purpura (ITP)
cythemias: leukocytosis; polycythemia vera; secondary polycythemia
Coagulation disorders (hypocoagulable and hypercoagulable conditions)
hypocoagulable: disseminated intravascular coagulation; hemophilia, congenital
factor VIII [hemophilia A] and IX [hemophilia B]; hypofibrinogenemia; von
Willebrand disease; platelet dysfunction, qualitative
hypercoagulable: heparin-induced thrombocytopenia; other coagulopathies (eg,
homocysteinemia, hypoplasminogenemia, antithrombin III, protein C/protein S
deficiency, Factor V Leiden, anticardiolipin antibodies, lupus anticoagulant,
prothrombin G20210A mutation)
reactions to blood components: ABO incompatibility/anaphylaxis; Rh
incompatibility/anaphylaxis; hemolysis, delayed; transfusion reaction; transfusion
contaminated with bacteria; transfusion-related acute lung injury (TRALI);
anaphylactoid reaction (IgA deficiency)
Traumatic, mechanical, and vascular disorders: mechanical injury to erythrocytes (eg, cardiac
valve hemolysis); disorders of the spleen; splenic rupture/laceration; splenic infarct;
splenic abscess; effects/complications of splenectomy (eg, sepsis due to encapsulated
bacteria); hypersplenism
Adverse effects of drugs on the hematologic and lymphoreticular systems: antiplatelet drugs,
antithrombin drugs (eg, dabigatran); chemotherapeutic agents; inhibitors of coagulation
factors; methemoglobinemia, acquired; propylthiouracil; tumor lysis syndrome; warfarin
Behavioral Health
Normal Processes
Psychodynamic and behavioral factors, related past experience (eg, transference,
personality traits)
Adaptive behavioral responses to stress and illness (eg, coping mechanisms)
Maladaptive behavioral responses to stress and illness (eg, drug-seeking behavior, sleep
deprivation)
Patient adherence: general adherence; adolescent adherence
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Psychotic disorders: brief psychotic disorder; delusional disorder; psychotic disorder due to
another medical condition; schizophrenia; schizoaffective disorder; substance-induced
psychotic disorder
Anxiety disorders: acute stress disorder; anxiety disorders (generalized anxiety disorder,
anxiety due to another medical condition, social phobia); hyperventilation syndrome;
obsessive-compulsive disorder; panic disorder with and without agoraphobia; phobic
disorders; post-traumatic stress disorder; separation anxiety disorder; substance-induced
anxiety disorder, trichotillomania
Mood disorders: major depressive disorder with and without psychotic features, with and
without seasonal pattern; major depressive disorder, postpartum, with and without
psychotic features, including screening; cyclothymic disorder; persistent depressive
disorder (dysthymia); bipolar disorder, manic/depressed/mixed; premenstrual dysphoric
disorder; bipolar and related disorder or depressive disorder due to another medical
condition; substance/medication-induced bipolar and related disorder or depressive
disorder (illegal or prescribed); suicidal ideation/attempt
Somatoform disorders: body dysmorphic disorder; conversion disorder, including psychogenic
seizures; dissociative disorders; illness anxiety disorder (hypochondriasis); malingering;
pain disorder; somatic symptom disorder
Factitious disorders: factitious disorder imposed on self
Eating disorders and impulse control disorders: anorexia nervosa; binge-eating disorder;
bulimia nervosa; eating disorder; disruptive, impulse-control, and conduct disorders (eg,
gambling, kleptomania, pyromania)
Disorders originating in infancy/childhood: reactive attachment disorder; attentiondeficit/hyperactivity disorder; speech sound disorder or language disorder; learning
disorder/dyslexia; intellectual developmental disorder and developmental delay,
undefined, including school problems, fetal alcohol syndrome; oppositional defiant
disorder, conduct disorder; autism spectrum disorder, Rett syndrome; psychoses with
origin specific to childhood; elimination disorders (incontinence, encopresis); tic
disorders/Tourette disorder
Personality disorders: antisocial personality disorder; avoidant personality disorder;
borderline personality disorder; dependent personality disorder; histrionic personality
disorder; narcissistic personality disorder; obsessive-compulsive personality disorder;
paranoid personality disorder; schizoid personality disorder
Psychosocial disorders/behaviors: adjustment disorder; grief response/bereavement, normal
and persistent complex; parent-child relational problems other than physical or emotional
abuse; other psychosocial stress
Sexual and gender identity disorders: gender dysphoria; psychosexual dysfunction
Substance use disorders: alcohol use disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal;
tobacco/nicotine use disorder/dependence/withdrawal; varenicline use; cannabis use
disorder/intoxication/dependence; hallucinogen use
disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal; inhalant use
disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal; opioid, heroin, including prescription drug,
use disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal; sedative, hypnotic, including
benzodiazepine and barbiturate use disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal;
stimulant, cocaine, methamphetamine use
disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal; other drugs of use disorders (eg, ecstasy,
PCP, bath salts)/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal; polysubstance use
disorder/intoxication/dependence/withdrawal
Nervous System & Special Senses
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes, including neural tube
derivatives, cerebral ventricles, and neural crest derivatives
Organ structure and function
spinal cord
gross anatomy and blood supply
spinal reflexes
brain stem (eg, cranial nerves and nuclei, reticular formation, anatomy and blood
supply, control of eye movements)
brain
gross anatomy and blood supply
higher function: cognition, language, memory, executive function
hypothalamic function
limbic system and emotional behavior
circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder
sensory systems
general sensory modalities, including sharp, dull, temperature, vibratory, and
proprioception
special sensory modalities, including vision, hearing, taste, olfaction, and balance
motor systems
brain and spinal cord (upper motoneuron)
basal ganglia and cerebellum
autonomic nervous system
peripheral nerves
Cell/tissue structure and function, including neuronal cellular and molecular
biology
axonal transport
excitable properties of neurons, axons, and dendrites, including channels
synthesis, storage, release, reuptake, and degradation of neurotransmitters and
neuromodulators
presynaptic and postsynaptic receptor interactions, trophic and growth factors
brain metabolism
glia, myelin
brain homeostasis: blood-brain barrier, cerebrospinal fluid formation and flow,
choroid plexus
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening,
Diagnosis, Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders: meningitis: bacterial (Actinomyces israelii; Haemophilus influenzae;
Listeria monocytogenes; Mycobacterium tuberculosis; Neisseria meningitidis;
Staphylococcus aureus, epidermidis; Streptococcus agalactiae; Streptococcus
pneumoniae); viral (adenovirus, arboviruses, echovirus and coxsackie A & B viruses,
polioviruses, herpes simplex virus, varicella zoster, human immunodeficiency virus,
lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus, measles virus, mumps virus, St. Louis encephalitis
virus, California encephalitis virus, Western equine encephalitis virus); fungal
(Blastomycosis dermatitidis, Cryptococcus neoformans/gattii); spirochetal (Borrelia
burgdorferi; Leptospira; Treponema pallidum, including neurosyphilis);
protozoal/helminths (Acanthamoeba, Naegleria fowleri, Strongyloides stercoralis,
Angiostrongylus cantonensis, Baylisascaris procyonis); encephalitis (herpesvirus [HSVI], varicella-zoster virus, Epstein-Barr virus, cytomegalovirus, mumps virus,
enterovirus, West Nile virus, St. Louis encephalitis virus, rabies virus, Eastern and
Western equine encephalitis virus, poliovirus, Taenia, Toxoplasma gondii); prion
disease (eg, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease); botulism (Clostridium botulinum), tetanus
(Clostridium tetani); CNS disorders associated with AIDS (eg, progressive multifocal
leukoencephalopathy)
immunologic and inflammatory disorders: myasthenia gravis, including thymoma;
multiple sclerosis; transverse myelitis
Neoplasms (cerebral, spinal, and peripheral): benign (meningioma, neurofibromatosis);
malignant (glioblastoma multiforme, astrocytoma, medulloblastoma, primary CNS
lymphoma); metastatic (eg, breast, lung, pancreatic, testicular, melanoma)
Cerebrovascular disease: arteriovenous malformations, ectatic cerebral vessels; transient
ischemic attack; stroke, thrombotic: cerebral artery occlusion/cerebral infarction;
stroke, embolic: cerebral embolism; stroke: intracerebral hemorrhage, including
subarachnoid hemorrhage, traumatic intracranial hemorrhage; cerebral artery
aneurysm; carotid artery stenosis/atherosclerosis/occlusion/dissection; vertebral artery
deficiency/dissection; subclavian steal syndrome; vascular dementia; hypertensive
encephalopathy; posterior reversible encephalopathy syndrome; venous sinus
thrombosis
Disorders relating to the spine, spinal cord, and spinal nerve roots: cauda equina syndrome;
spinal artery thrombosis/embolus/infarct; spinal cord compression; spinal cord
transection, paraplegia and quadriplegia, acute and chronic effects (eg, autonomic
dysreflexia); spinal stenosis (cervical, lumbar); syringomyelia
Cranial and peripheral nerve disorders
cranial nerve injury/disorders: cranial nerve injury; Bell palsy; anisocoria, miosis,
mydriasis; internuclear ophthalmoplegia; nystagmus and other irregular eye
movements; vestibular neuritis, labyrinthitis; ptosis of the eyelid; Horner syndrome
peripheral nerve/plexus injury/disorders: peripheral nerve injury, including brachial
plexus; carpal/cubital/tarsal/peroneal tunnel syndrome; mononeuritis, Guillain-Barré
syndrome; Miller Fisher syndrome; neuropathy (eg, Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease);
herpes zoster
Neurologic pain syndromes: complex regional pain syndrome (reflex sympathetic
dystrophy, causalgia); fibromyalgia; postherpetic neuralgia; phantom limb
pain/syndrome; thalamic pain syndrome; trigeminal neuralgia
Degenerative disorders/amnestic syndromes: Alzheimer disease; frontotemporal
dementia, including progressive supranuclear palsy, Lewy body disease; mild
neurocognitive disorder, mild cognitive impairment
Global cerebral dysfunction: altered states of consciousness; delirium; coma/brain death
Neuromuscular disorders: amyotrophic lateral sclerosis/spinal muscular atrophy; muscular
dystrophy (eg, Duchenne, myotonic); muscle channelopathies (eg, hypokalemic period
paralysis)
Movement disorders: acute dystonia; adult tic disease; essential tremor; Huntington
disease; Parkinson disease, including Parkinson dementia
Metabolic disorders: adrenoleukodystrophy; metabolic encephalopathy
Paroxysmal disorders: headache, including migraine, mixed, tension, ice-pick, cluster,
medication withdrawal, caffeine withdrawal; seizure disorders, including generalized
tonic-clonic, partial, absence, febrile
Sleep disorders: cataplexy and narcolepsy; circadian rhythm sleep-wake disorder;
insomnia, primary; sleep terror disorder and sleepwalking; REM sleep behavior
disorder; restless legs syndrome
Traumatic and mechanical disorders and disorders of increased intracranial pressure:
anoxic brain damage, cerebral hypoxia; epidural, subdural hematoma (cerebral and
spinal); intraparenchymal hemorrhage, traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhage; cerebral
edema; pseudotumor cerebri (idiopathic intracranial hypertension); torticollis/cervical
dystonia; hydrocephalus, including normal-pressure; traumatic brain injury
(concussion)/postconcussion syndrome (dementia pugilistica); traumatic brain syndrome
Congenital disorders: Friedreich ataxia; neural tube defects (eg, spina bifida,
holoprosencephaly, anencephaly); microcephaly; Sturge-Weber syndrome; tuberous
sclerosis, von Hippel-Lindau disease; hydrocephalus, obstructive (Arnold-Chiari)
Adverse effects of drugs on the nervous system: acute dystonic reaction; drug-induced
meningitis (eg, NSAIDs, sulfa drugs); drug-induced neuropathy (eg, vincristine,
isoniazid, metronidazole); extrapyramidal adverse effects (eg, akathisia, dystonia,
drug-induced parkinsonism); neuroleptic malignant syndrome; poisoning by
psychotropic agents, including antidepressants; serotonin syndrome; tardive
dyskinesia
Disorders of the eye and eyelid
infectious and inflammatory disorders of the eye: blepharitis/eyelid inflammation;
chalazion; chorioretinitis; conjunctivitis (adenovirus)/keratoconjunctivitis;
dacryocystitis; endophthalmitis; hordeolum; iridocyclitis; optic neuritis; periorbital
cellulitis; uveitis
neoplasms of the eye: melanoma; retinoblastoma
disorders of the eye and eyelid, structural: cataract; glaucoma; lacrimal system
disorders; pterygium; refractive disorders (presbyopia, myopia, hyperopia,
astigmatism)
disorders of the pupil, iris, muscles (extraocular): amblyopia; strabismus
disorders of the retina: hypertensive retinopathy; macular degeneration; papilledema;
retinal detachment; retinitis pigmentosa; vascular disorders affecting the retina,
including central retinal artery embolus, retinal hemorrhage, amaurosis fugax,
embolus, carotid artery stenosis, central retinal vein occlusion; visual
impairment/blindness, night blindness
traumatic and mechanical disorders: black eye; burn of the eye and adnexa; corneal
abrasion, ulcer; dislocated lens; foreign body in eye; hyphema; injury to optic nerve
and pathways; laceration of the eye and eyelid; ocular open wounds; orbital
fracture; subconjunctival hemorrhage
adverse effects of drugs on the eyes: ethambutol; hydroxychloroquine; prednisone
Disorders of the ear
infectious and inflammatory disorders of the ear: chondritis; mastoiditis; otitis,
externa, media, interna, serous, suppurative, malignant otitis externa
neoplasms: acoustic neuroma, neurofibromatosis type 2; cholesteatoma
hearing loss/deafness: hearing loss, including noise-induced; otosclerosis; tinnitus
disorders of balance and spatial orientation: Ménière disease; motion sickness; vertigo,
including benign positional vertigo
traumatic and mechanical disorders: barotrauma; foreign body in ear; impacted
cerumen; laceration, avulsion; perforation of tympanic membrane; eustachian
tube disorders
adverse effects of drugs on the ear: antineoplastic agents, including cisplatin;
aminoglycosides; furosemide; salicylates
Skin & Subcutaneous Tissue
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and neonatal changes
Organ structure and function, including barrier function, thermal regulation
Cell/tissue structure and function, eccrine function
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life (eg, senile purpura, male
pattern baldness, postmenopausal hair changes)
Skin defense mechanisms and normal flora
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders and infestations
bacterial: cellulitis, erysipelas, impetigo, staphylococcal scalded skin syndrome;
abscess, cutaneous, including septic abscess; anthrax (Bacillus anthracis);
carbuncle; folliculitis; pilonidal cyst, infected; pyoderma gangrenosum; MSSA
and MRSA skin infections; mycobacterial infections (eg, leprosy, draining
sinus); scarlet fever (group A Streptococcus)
viral: herpes simplex type 1 & type 2, herpes zoster, Ramsay-Hunt syndrome;
molluscum contagiosum; hand-foot-and-mouth disease; herpangina;
parvovirus; chickenpox, erythema infectiosum (fifth disease), rubella, measles,
roseola (exanthema subitum); verrucae vulgaris
fungal (deep and superficial): candidiasis, skin; dermatophytosis, tinea corporis;
dermatomycoses; diaper rash; onychomycosis
parasitic: cutaneous larva migrans; cutaneous leishmaniasis
infestations, nonvenomous bites, stings: scabies; lice; insect bites, including bed
bugs
immunologic and inflammatory disorders
papulosquamous and eczematous dermatoses: psoriasis; lichen planus and
lichenoid dermatoses; allergic/irritant contact dermatitis (eg, nickel);
dermatoses caused by plants (poison ivy, poison oak)
vesiculobullous disorders: epidermolysis bullosa; dermatitis herpetiformis;
pemphigus; pemphigoid
urticaria, erythema, exanthema, and purpura: erythema nodosum; atopic
dermatitis; pityriasis rosea; urticaria; Stevens-Johnson syndrome, erythema
multiforme, toxic epidermal necrolysis
autoimmune disorders: vitiligo
Neoplasms
benign neoplasms, cysts and other skin lesions: actinic keratoses; cysts, including
epidermal; hemangiomas; lipoma; pigmented nevi; seborrheic keratosis;
xanthomas
malignant neoplasms: basal cell carcinoma; squamous cell carcinoma; melanoma,
including genital; Kaposi sarcoma; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma, mycosis fungoides
Adnexal disorders (hair and hair follicles, nails, sweat glands, sebaceous glands, oral
mucous membranes)
disorders of the hair and hair follicles: alopecia; seborrhea capitis/seborrheic dermatitis;
tinea barbae and capitis
disorders of the nails (including ingrowing nail)
disorders of sweat and sebaceous glands: acne vulgaris; hidradenitis suppurativa;
hyperhidrosis; ichthyosis; rosacea
Oral disease: aphthous ulcers (stomatitis, canker sores); leukoplakia
Disorders of pigmentation: albinism; lentigo
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: animal bites (dogs, cats, etc); burns or wounds affecting
the skin or subcutaneous tissue (eg, sunburn, other including blast injuries and burns);
cauliflower ear; effects of ultraviolet light; keloids; tattoo; thermal injury, perniosis,
frostbite; ulcers, decubitus
Congenital disorders: xeroderma pigmentosum; benign lesions in neonates, infants,
children (eg, congenital nevi)
Adverse effects of drugs on skin and subcutaneous tissue: drug reactions, eruptions,
including local reaction to vaccine
Musculoskeletal System
Normal processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
Organ structure and function
Cell/tissue structure and function
biology of bones, joints, tendons, skeletal muscle, cartilage
exercise and physical conditioning/deconditioning
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, inflammatory, and immunologic disorders
infectious disorders: gangrene, dry and wet, clostridial myonecrosis (Clostridium
perfringens); discitis; myositis, infective; necrotizing fasciitis; osteomyelitis; septic
arthritis; spondylitis, tuberculous
immunologic disorders: ankylosing spondylitis; dermatomyositis/polymyositis;
juvenile idiopathic arthritis; rheumatoid arthritis, Felty syndrome; psoriatic
arthropathy
inflammatory disorders: adhesive capsulitis of shoulder (frozen shoulder syndrome);
ankylosis/spondylopathy (inflammatory); bursitis; fasciitis; osteochondritis,
osteochondritis dissecans; tendinitis, supraspinatus syndrome, enthesopathy of spine,
elbow, ankle; temporomandibular joint disorders; fibrositis, myofascial pain
syndrome; synovitis; tenosynovitis; myositis
Neoplasms: benign neoplasms (e.g., ganglion cyst); malignant neoplasms of bone (eg,
osteosarcoma, sarcoma, leiomyosarcoma, rhabdosarcoma); metastases to bone,
secondary malignant neoplasm of bone
Degenerative and metabolic disorders
degenerative/metabolic disorders of bone, tendon, and cartilage: chondromalacia; disc
degeneration, herniated disc; Legg-Calvé-Perthes disease; Osgood-Schlatter disease;
osteodystrophy; osteomalacia; osteonecrosis (avascular), bone infarct; osteoporosis;
osteopenia; osteitis deformans (Paget disease of bone); pathologic fracture;
radiculopathies; spondylolisthesis/spondylosis (degenerative)
degenerative/metabolic disorders of joints: gout, gouty arthritis, pseudogout; joint
effusion; osteoarthritis
degenerative/metabolic disorders of muscles, ligaments, fascia: Dupuytren contracture;
muscle calcification and ossification; muscle wasting and diffuse atrophy;
rhabdomyolysis
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: amputation and care of amputees; backache, including
low back pain; blast injuries; compartment syndrome; contractures, hospital-acquired;
contusions; dislocations; fractures; sprains, strains; kyphoscoliosis, scoliosis; rotator cuff
syndrome; slipped capital femoral epiphysis; dislocation of hip
Congenital disorders: achondroplasia/dwarfism; disorders of limb development (HOX gene
mutation, phocomelia); developmental dysplasia of the hip; dislocation of hip in
infantile spinal muscular atrophy; genu valgum or varum; foot deformities (flat foot,
valgus/varus deformities); osteogenesis imperfecta; McArdle disease; mitochondrial
myopathies
Adverse effects of drugs on the musculoskeletal system: drug-induced myopathy (eg,
steroids, statins, cocaine, AZT); malignant hyperthermia
Cardiovascular System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal transitional changes
Organ structure and function
chambers, valves
cardiac cycle, mechanics, heart sounds, cardiac conduction
hemodynamics, including blood volume and systemic vascular resistance
circulation in specific vascular beds, including pulmonary and coronary
Cell/tissue structure and function
heart muscle, metabolism, oxygen consumption, biochemistry, and secretory function
(eg, atrial natriuretic peptide)
endothelium and secretory function, vascular smooth muscle, microcirculation, and
lymph flow
neural and hormonal regulation of the heart, blood vessels, and blood volume,
including responses to change in posture, exercise, and tissue metabolism, and
autonomic responses
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders: bacterial endocarditis, myocarditis
immunologic and inflammatory disorders: atherosclerosis (eg, atherosclerosis of the
aorta)
Neoplasms: myxoma, metastases
Dysrhythmias: premature beats (PACs, PVCs); atrial flutter/fibrillation; multifocal atrial
tachycardia; paroxysmal tachycardias; ventricular tachycardia/fibrillation; wide complex
tachycardia; torsades de pointes; bradycardias; atrioventricular block (first-, second-,
third-degree); conduction disorder (LBBB, RBBB); cardiac arrest; sick sinus syndrome;
prolonged QT syndrome; Wolff-Parkinson-White syndrome; carotid sinus hypersensitivity;
pacemaker dysfunction, including failure to sense, capture
Heart failure: chordae tendineae rupture; congestive heart failure; cor pulmonale; diastolic
dysfunction; systolic dysfunction; mitral valve dysfunction; heart failure secondary to
myocardial infarction; high-output heart failure, including thyrotoxicosis-induced,
anemia-induced; tachycardia-induced; cardiogenic pulmonary edema
Ischemic heart disease: acute coronary syndrome, acute myocardial infarction; angina
pectoris, stable and unstable/coronary artery disease/coronary insufficiency;
coronary artery spasm
Diseases of the myocardium: cardiomyopathy, dilated, including alcoholic, viral, takotsubo;
cardiomyopathy, obstructive hypertrophic; cardiomyopathy, familial dilated;
cardiomyopathy, restrictive; hypertensive heart disease, left ventricular hypertrophy,
right ventricular hypertrophy; complications of myocardial infarction; nontraumatic
tamponade post-myocardial infarction; papillary muscle rupture/dysfunction; ventricular
free wall rupture; myocarditis
Diseases of the pericardium: chronic constrictive pericarditis; pericardial effusion; pericardial
tamponade; acute pericarditis; pericarditis, following myocardial infarction, surgery,
trauma
Valvular heart disease: valve disorders, mitral/aortic/tricuspid, pulmonic (eg,
regurgitation, stenosis, prolapse, insufficiency, vegetation); functional murmurs;
rheumatic heart disease; complications of artificial valves
Hypotension: orthostatic hypotension
Hypertension: elevated blood pressure reading without diagnosis of hypertension; essential
hypertension; malignant hypertension; secondary hypertension
Dyslipidemia: hypercholesterolemia; hyperlipidemia; hypertriglyceridemia;
lipoproteins/lipoprotein lipase deficiency
Vascular disorders
disorders of the great vessels: aneurysm, aortic (abdominal/thoracic), dissection,
ruptured; aneurysm, iliac, other peripheral vascular, ruptured; aortoiliac disease
peripheral arterial vascular disease: arterial embolus/thrombosis; arteriovenous
fistula; atheroembolic disease; claudication; cholesterol emboli; hypertensive
vascular disease; peripheral arterial disease; thromboangiitis obliterans
diseases of the veins: deep venous thrombosis, venous thromboembolism;
phlebitis/thrombophlebitis; varicose veins; venous insufficiency; stasis ulcers,
stasis dermatitis
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: ventricular puncture; myocardial contusion;
myocardial rupture; traumatic aortic dissection; traumatic tamponade
Congenital disorders, including disease in adults: anomalous left coronary artery; atrial
septal defect; coarctation of the aorta; endocardial cushion defect; patent foramen
ovale; patent ductus arteriosus; tetralogy of Fallot; transposition of the great vessels;
ventricular septal defect
Adverse effects of drugs on the cardiovascular system: adriamycin; cocaine, amphetamine,
PCP; ACE inhibitors, calcium channel blockers, alpha blockers, minoxidil
Respiratory System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
Organ structure and function
airways, including mechanics and regulation of breathing
lung parenchyma, including ventilation, perfusion, gas exchange
pleura
nasopharynx, sinuses
Cell/tissue structure and function, including surfactant formation, and alveolar structure
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Pulmonary defense mechanisms and normal flora
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders of the upper airways: acute
upper respiratory infection; viral infections (adenovirus, coronaviruses,
coxsackievirus, influenza virus, parainfluenza virus, rhinoviruses); sinusitis;
nasopharyngitis; epiglottitis; Bordetella pertussis pneumonia; croup; acute
laryngitis; acute laryngotracheitis; tracheitis; pharyngitis; streptococcal throat
infections; tonsillitis; peritonsillar abscess; rhinitis, allergic, chronic; ulcers of nasal
cavity/sinuses
infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders of the lower airways: hospitalacquired pneumonia; ventilator-associated pneumonia, community-acquired
pneumonia, acute bronchiolitis; bronchiolitis obliterans with organizing pneumonia
(BOOP); anthrax, pulmonary (Bacillus anthracis); aspiration pneumonia, pneumonitis;
bronchitis, acute; bronchopneumonia; pneumonia (Burkholderia pseudomallei,
Chlamydophila pneumoniae, Coxiella burnetii, Francisella tularensis, Haemophilus
influenzae, Klebsiella pneumoniae, Legionella, Moraxella catarrhalis, Mycoplasma
pneumoniae, Pseudomonas aeruginosa, Streptococcus, MSSA, MRSA, other
gram‐negative bacteria); viral infection (eg, influenza A, B, adenovirus, H1N1,
respiratory syncytial virus, parainfluenza virus); fungal infection (aspergillosis, including
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and aspergilloma, histoplasmosis,
coccidioidomycosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii); pulmonary tuberculosis; lung abscess;
viral infection (eg, influenza A, B, adenovirus, respiratory syncytial virus,
parainfluenza virus, avian influenza virus); fungal infection (aspergillosis, including
allergic bronchopulmonary aspergillosis and aspergilloma, histoplasmosis,
coccidioidomycosis, Pneumocystis jirovecii)
Neoplasms
benign neoplasms: upper airways (eg, vocal cord polyps, nasal polyps, juvenile
papillomatosis); lungs and pleura (eg, solitary pulmonary nodule, bronchial
carcinoid tumors)
malignant neoplasms
upper airways: lip, oral cavity, and pharynx; head and neck cancer; larynx;
trachea
lower airways and pleura: malignant neoplasms of bronchus and/or lung (squamous
cell, adenocarcinoma, large cell, small cell); malignant neoplasms of pleura
(mesothelioma); secondary malignant neoplasms of lung; secondary malignant
neoplasms of pleura
metastatic neoplasms including pleural
Obstructive airway disease: asthma, reactive airway disease; bronchiectasis; chronic airway
obstruction; chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), chronic bronchitis,
emphysema
Pneumoconiosis/fibrosing/restrictive pulmonary disorders/interstitial lung disease:
pneumoconiosis; asbestosis; silicosis; silo-filler's lung, byssinosis, bagassosis,
berylliosis; hypersensitivity pneumonitis; hypereosinophilic syndromes, Loeffler
syndrome; interstitial pneumonia, usual (UIP), desquamative (DIP), nonspecific
Respiratory failure/respiratory arrest and pulmonary vascular disorders: acute respiratory
distress syndrome (ARDS); pulmonary hypertension; pulmonary vascular disorders,
arteriovenous fistula; pulmonary edema, pulmonary cause and unspecified; pulmonary
embolism; air and fat embolism; respiratory failure due to enteral feeding
Metabolic, regulatory, and structural disorders: disorders of gas exchange; hypoventilation;
hypoxia; pulmonary alveolar proteinosis; ventilation-perfusion imbalance
Disorders of the pleura, mediastinum, and chest wall: chylothorax; costochondritis;
empyema; hemothorax; mediastinitis; pleural effusion; pleuritis;
pneumomediastinum; pneumothorax
Traumatic and mechanical disorders
upper airways: epistaxis; barotrauma, sinus; laryngeal/pharyngeal obstruction;
tracheoesophageal fistula; tracheal stenosis; tracheomalacia; trauma (eg, tracheal
injury); foreign body (nose, pharynx, larynx, trachea); traumatic/mechanical
disorders of the nasal cavity/sinuses (eg, septal perforation)
lower airways and pleura: atelectasis; diaphragm/chest wall injury; drowning and neardrowning; foreign body, upper and lower respiratory tract; penetrating chest wounds;
pulmonary contusion; sleep apnea, obstructive and central; hypoventilation
syndrome, obesity-hypoventilation syndrome
Congenital disorders: bronchogenic cysts; congenital cysts; congenital diaphragmatic
hernia; pulmonary sequestration; immotile cilia syndrome
Adverse effects of drugs on the respiratory system: bleomycin, amiodarone; adverse
effects of 100% oxygen; acute effects of tobacco/nicotine, inhalants, cocaine
Gastrointestinal System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
Organ structure and function
anatomy of the alimentary canal, including mouth, pharynx, esophagus, stomach, small
intestine, large intestine, anus, peritoneal cavity
liver and biliary system, including enterohepatic circulation
salivary glands and exocrine pancreas
gastrointestinal motility, including defecation digestion and absorption
Cell/tissue structure and function
endocrine and neural regulatory functions, including GI hormones (eg, gastrin)
salivary, gastrointestinal, pancreatic, hepatic secretory products, including enzymes,
proteins, bile salts, and processes
synthetic and metabolic functions of hepatocytes
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Gastrointestinal defense mechanisms and normal flora
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders
bacterial: pseudomembranous colitis (Clostridium difficile); enteritis/enteric infections
(includes gastroenteritis) (eg, Staphylococcus aureus, Escherichia coli, Listeria
monocytogenes, Yersinia enterocolitica, Campylobacter species, Vibrio cholerae,
Salmonella species, Shigella species, traveler's/infectious diarrhea); hepatic
abscess, subhepatic abscess, subphrenic abscess; peritonitis, primary and
secondary; Whipple disease
viral: infectious esophagitis (eg, CMV, herpes); hepatitis A, B, C, D, E; coxsackievirus
enteritis/colitis; Echovirus enteritis/colitis; rotavirus enteritis; mumps;
gingivostomatitis, herpetic
fungal: thrush
parasitic: Cryptosporidium, Cyclospora, Entamoeba histolytica, Giardia, Isospora belli,
Strongyloides stercoralis
immunologic and inflammatory disorders: autoimmune hepatitis; celiac disease;
eosinophilic esophagitis; granulomatous enteritis; inflammatory bowel disease,
including Crohn disease, regional enteritis, microscopic colitis (collagenous and
lymphocytic colitis), ulcerative colitis, toxic megacolon
Neoplasms
benign neoplasms, including polyps, cysts: stomach; small intestine; colon, rectum, and
anus, including polyps
malignant neoplasms and pre-malignant conditions: oral cancer (eg, lips, mouth, tongue,
salivary glands); esophageal, squamous and adenocarcinoma; Barrett esophagus;
gastrinoma, Zollinger-Ellison syndrome; gastrointestinal carcinoid tumors;
gastrointestinal stromal tumors; small intestine; stomach, adenocarcinoma,
lymphoma, MALT; colon, rectum, anus; hereditary colon cancer syndromes, familial
adenomatous polyposis (eg, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome, Gardner syndrome, Turcot
syndrome, ); MUTYH-associated polyposis; gallbladder, cholangiocarcinoma,
adenocarcinoma of the ampulla of Vater; liver, including hepatoma; peritoneal
cancer, including metastatic studding with cancer; pancreas
metastatic neoplasms
Signs, symptoms, and ill-defined disorders: upper gastrointestinal bleeding; lower
gastrointestinal bleeding; constipation; diarrhea; hematochezia; bright red rectal
bleeding; melena; nausea, vomiting, rumination
Disorders of the oral cavity, salivary glands, and esophagus
oral cavity and salivary glands: abscessed tooth; dental caries; malocclusion;
disorders of the salivary glands (eg, stones, sialadenitis, parotitis)
esophagus: achalasia and cardiospasm; dysphagia; diverticulum (eg, Zenker);
esophageal periapical abscess without sinus; esophagitis/esophageal reflux
(GERD); esophagitis, pill; Mallory-Weiss syndrome; paraesophageal (hiatal) hernia;
stricture and stenosis of esophagus
Disorders of the stomach, small intestine, colon, rectum, anus
stomach: dyspepsia/hyperacidity; gastric ulcer; gastritis; peptic ulcer; peptic ulcer
perforation; gastroparesis
small intestine, colon: appendicitis; angiodysplasia; diverticula, diverticulitis,
diverticulosis; duodenitis, duodenal ulcer, peptic ulcer; gastroenteritis and colitis
(noninfectious); granulomatous enterocolitis; Hirschsprung disease; impaction of
intestine; intestinal obstruction/stricture; intussusception; irritable colon/irritable
bowel syndrome; mesenteric ischemia/ischemic bowel/ischemic colitis; necrotizing
enterocolitis; paralytic ileus; volvulus; malnutrition and malabsorption, including
lactose intolerance, short bowel syndrome
rectum and anus: abscess of anal and rectal regions; anal fissure; anal fistula; ulcer;
fecal incontinence; hemorrhage (rectum, anus); proctitis; hemorrhoids; rectal
prolapse
Disorders of the liver and biliary system, noninfectious
liver: cirrhosis; Dubin-Johnson, Rotor syndromes; end-stage liver disease, including
indications for transplantation; Gilbert syndrome, Crigler-Najjar syndrome; hepatic
coma/hepatic encephalopathy; hepatitis, noninfectious; hepatitis, fatty liver,
alcoholic; hepatorenal syndrome; hepatopulmonary syndrome; jaundice; nonalcoholic fatty liver disease; portal hypertension/esophageal varices
biliary system: bile duct obstruction/cholestasis; cholangitis, including ascending;
choledocholithiasis; cholelithiasis/cholecystitis; cholestasis due to parenteral
nutrition; gallstone ileus; Mirizzi syndrome; primary biliary cirrhosis; primary
sclerosing cholangitis
Disorders of the pancreas: pancreatitis, acute; pancreatitis, chronic; pancreatitis,
hereditary; pancreatic cyst/pseudocyst; pancreatic duct obstruction; pancreatic
insufficiency
Disorders of the peritoneal cavity: ascites
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: abdominal wall defects; adhesions, postsurgical;
digestive system complications of surgery; post-gastric surgery syndromes (eg, blind loop
syndrome, adhesions); duodenal tear; foreign body in digestive system; inguinal, femoral,
and abdominal wall hernias; open wound, abdominal; perforation of hollow viscus and
blunt trauma; perforation/rupture of esophagus (Boerhaave syndrome); umbilical hernia
Congenital disorders: annular pancreas, biliary atresia, cleft lip and palate, esophageal
atresia, malrotation without volvulus, Meckel diverticulum, pyloric stenosis,
tracheoesophageal fistula
Adverse effects of drugs on the gastrointestinal system: drug-induced changes in motility
(chronic laxative abuse, opioids); drug-induced gastritis, duodenitis, peptic ulcer disease
(NSAIDs); drug-induced hepatitis (eg, acetaminophen, isoniazid); drug-induced
pancreatitis (eg, thiazide diuretics)
Renal & Urinary System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes
Organ structure and function
kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra
glomerular filtration and hemodynamics
urine concentration and dilution
renal mechanisms in acid-base balance
renal mechanisms in body fluid homeostasis
micturition
Cell/tissue structure and function
renal metabolism and oxygen consumption
tubular reabsorption and secretion, including transport processes and proteins
hormones produced by or acting on the kidney (eg, renin, aldosterone, angiotensin II,
vasopressin)
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders
upper urinary tract: granulomatous pyelonephritis; perinephric abscess;
pyelonephritis; pyonephrosis; renal abscess; renal tuberculosis
lower urinary tract and urinary tract infections of unspecified location: cystitis;
chlamydial and nonchlamydial
immunologic and inflammatory disorders
upper urinary tract
glomerular disorders: Alport syndrome; glomerular disease due to hepatitis
B, C; glomerulonephritis, including poststreptococcal; IgA nephropathy;
lupus nephritis; minimal change disease; nephrotic syndrome; thin
basement membrane disease
tubular interstitial disease: acute tubular necrosis (ATN); acute
interstitial nephritis; papillary necrosis; HIV nephropathy
lower urinary tract: interstitial cystitis
Neoplasms
benign neoplasms and cysts: polycystic kidney disease
malignant neoplasms: renal (eg, Wilms tumor/nephroblastoma, renal cell carcinoma,
renal tumors associated with congenital/hereditary conditions); urinary bladder and
collecting system
Signs, symptoms, and ill-defined disorders: dysuria; hematuria; oliguria, anuria; proteinuria
Metabolic and regulatory disorders: acute kidney injury; renal insufficiency; azotemia,
uremic syndrome; chronic kidney disease, including end-stage renal disease;
cystinuria; Fanconi syndrome; hypertensive renal disease (renal complications of
hypertension); renal calculi, ureteral calculi, nephrolithiasis; renal tubular acidosis
Vascular disorders: renal artery stenosis (atherosclerosis, fibromuscular dysplasia,
nephrosclerosis); renal vein thrombosis; renal infarction
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: bladder rupture; neurogenic bladder; obstructive
uropathy; posterior urethral valves; renal laceration; renal vascular injury; ureteral
laceration/avulsion/disruption; urethral diverticulum; urethral/ureteral
obstruction/stricture/prolapse; urinary incontinence, including secondary enuresis;
vesicoureteral reflux
Congenital disorders: double ureters/ureteral duplication/double collecting system;
horseshoe kidney; hydronephrosis/reflux; renal agenesis, renal hypoplasia, renal
dysplasia; single kidney
Adverse effects of drugs on the renal and urinary system: ACE inhibitors; aminoglycosides;
amphotericin B; cisplatin; furosemide; gadolinium (nephrogenic systemic fibrosis);
heroin; iodinated contrast dye; lithium; NSAIDs; penicillins; sulfa drugs; tenofovir; drug -
induced urinary retention
Pregnancy, Childbirth, & the Puerperium
Normal Processes
Organ structure and function: pregnancy, including fertilization, implantation, development
of embryo, labor and delivery, the puerperium, lactation, gestational uterus, placenta
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Prenatal care
preconception counseling and care: folate deficiency prevention; immunizations;
nutritional exam, including vitamins; Rh screening
prenatal risk exam/prevention: adolescent pregnancy; antepartum fetal
evaluation, including biophysical profile; genetic screening; α-fetoprotein; diabetes
mellitus; neural tube defects; Rh isoimmunization
supervision of normal pregnancy: exam of gestational age; iron deficiency
prevention; nutrition, including weight management; surveillance, including
ultrasonography and exam of fetal growth; vitamin deficiency prevention;
infections, maternal, fetal, newborn (focus on prevention and screening):
cytomegalovirus, coxsackievirus, hepatitis B virus, herpes simplex viruses, HIV,
influenza virus, parvovirus B19 virus, rubella virus, varicella-zoster virus, Chlamydia
trachomatis, Treponema pallidum, Streptococcus agalactiae, Toxoplasma gondii,
amnionitis; asymptomatic urinary tract infection
Obstetric complications: abortion, induced, septic, missed, spontaneous, threatened; acute
fatty liver of pregnancy; anemia of pregnancy, sickle cell disease, thalassemia in
pregnancy; antepartum hemorrhage, including third-trimester bleeding; cardiomyopathy
of pregnancy; cervical incompetence, cervical shortening; cholestasis of pregnancy,
intrahepatic; congenital abnormalities, maternal (eg, bicornuate uterus); ectopic
pregnancy; fetal abnormality affecting management of mother (eg, hydrocephalus, spina
bifida); fetal growth restriction; gestational diabetes; maternal mortality; multiple
gestation; placental abnormalities (abruptio placentae, placenta previa, premature
separation of placenta); polyhydramnios, oligohydramnios; preeclampsia, eclampsia,
HELLP syndrome, gestational hypertension; prolonged pregnancy; Rh isoimmunization
affecting management of mother; vomiting in pregnancy (morning sickness, hyperemesis
gravidarum); trauma in pregnancy; infections complicating pregnancy
Labor and delivery: labor and delivery, uncomplicated; labor and delivery, complicated,
including shoulder dystocia; cesarean delivery, including complications; cord
compression, cord prolapse; fetal malpresentations (eg, breech); intrapartum fetal
evaluation, including fetal heart tones; intrapartum prophylaxis (eg, HIV, Chlamydia,
gonococcal prophylaxis); premature rupture of membranes; preterm (before 37 weeks'
gestation) and postdates labor and delivery; threatened preterm labor
Puerperium, including complications: lactation problems; breast-feeding problems; lochia;
postpartum cardiomyopathy; postpartum blues; postpartum hemorrhage; postpartum
sepsis; retained placenta, products of conception (eg, placenta accreta); uterine atony
Newborn (birth to 4 weeks of age)
normal newborn
examination of liveborn at admission to hospital
screening, newborn
disorders of the newborn: screening, newborn; ABO incompatibility in newborn;
hemolytic disease due to Rh incompatibility; birth asphyxia syndrome (liveborn
neonate); birth trauma (eg, cord compression, brachial palsy, lacerations); drug
withdrawal syndrome in newborn; feeding problems in newborn; fetal growth and
development abnormalities, including fetal growth restriction; gastrointestinal
obstruction; hypocalcemia of newborn; infections, congenital or peripartum
(cytomegalovirus, herpes simplex viruses, HIV, hepatitis B, rubella virus, parvovirus
B19 virus, varicella zoster virus, Chlamydia trachomatis, Streptococcus agalactiae,
Treponema pallidum, Toxoplasma gondii); intrapartum fetal distress/death
including stillborn; jaundice, fetal/neonatal/perinatal; laryngomalacia; macrosomia
(large for gestational age); meconium aspiration syndrome; neonatal acne; neonatal
Candida infection (thrush); neonatal hypoglycemia; neonatal conjunctivitis and
dacryocystitis; ophthalmic gonorrhea; phenylketonuria; premature infant; postterm infant; pseudomembranous colitis of infancy; respiratory distress syndrome
(hyaline membrane disease); respiratory problems after birth (eg,
bronchopulmonary dysplasia, tracheomalacia; tracheoesophageal fistula in
neonates); retinitis of prematurity; seizures in newborn; sudden infant death
syndrome (SIDS), apparent life-threatening event (ALTE); tetanus neonatorum
Congenital disorders, neonatal: congenital malformations and anomalies; neonatal
hydrocele
Adverse effects of drugs on pregnancy, childbirth, and the puerperium: alcohol, tobacco,
and other drugs (ATOD); prenatal radiation exposure; teratology (eg, ACE inhibitors,
SSRIs, warfarin, infections, toxins)
Systemic disorders affecting pregnancy, labor and delivery, and puerperium:
appendicitis; asthma; carpal tunnel syndrome in pregnancy; cirrhosis; deep venous
thrombosis (DVT); diabetes mellitus; heart failure, valvular heart disease;hypertension;
myasthenia gravis; obesity; pancreatitis; psychiatric disorders; renal calculus/calculi;
renal failure/renal disease, including SLE; seizure disorders; thyroid disorders,
hypothyroidism, hyperthyroidism
Female Reproductive System & Breast
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and perinatal changes, gametogenesis
Organ structure and function
female structure, including breast
female function (eg, ovulation, menstrual cycle, puberty)
intercourse, sexual response
Cell/tissue structure and function: hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, sex steroids,
and gestational hormones
Reproductive system defense mechanisms and normal flora
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Breast
infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders: breast abscess; inflammatory
disease of breast, fat necrosis; mastitis; nipple discharge
neoplasms
benign and undefined neoplasms: breast cyst, solitary; fibrocystic changes;
fibroadenoma; hypertrophy of breast; intraductal papilloma
malignant neoplasms (including screening): breast cancer; intraductal carcinoma;
Paget disease of breast; phyllodes tumors
Female reproductive system
infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders: bacterial vaginosis; Bartholin gland
abscess; cellulitis, pelvic; candidiasis of the vulva or vagina; lichen sclerosus; sexually
transmitted infections and exposure; cervicitis and endocervicitis; chancroid
(Haemophilus ducreyi); genital herpes; gonorrhea (Neisseria gonorrhoeae); human
papillomavirus infection, genital/venereal/anal warts, condylomata acuminata;
lymphogranuloma venereum (Chlamydia trachomatis), non-lymphogranuloma
venereum; pelvic inflammatory disease; Fitz-Hugh–Curtis syndrome; salpingitis and
oophoritis; syphilis (Treponema pallidum); trichomoniasis (Trichomonas vaginalis);
urethritis; vaginitis; vulvovaginitis
Neoplasms of the cervix, ovary, uterus, vagina, and vulva
benign neoplasms and cysts: abnormal Pap smear; benign neoplasm of ovary;
endocervical and endometrial polyps; leiomyomata uteri; ovarian cyst
malignant and precancerous neoplasms: cervical cancer; HPV causing cancer; cervical
dysplasia, HPV causing dysplasia; endometrial hyperplasia; endometrial/uterine
cancer; gestational trophoblastic disease (hydatidiform mole); ovarian cancer;
vulvar dysplasia and cancer
Fertility and infertility: assisted reproductive techniques (ART); contraception (eg, oral
contraceptives, IUD, vaginal cap, cervical sponge, diaphragm, implant, morning-after
pill, male and female condoms); female infertility; gonadal dysgenesis 45,X (Turner
syndrome); sterilization; tubal factors; infertility
Menopause: ovarian failure, premature menopause; perimenopause; premenopausal
menorrhagia; postmenopausal atrophic vaginitis (vaginal atrophy); postmenopausal
bleeding; vasomotor symptoms
Menstrual and endocrine disorders: abnormal uterine bleeding, including
perimenopausal; absence of menstruation (primary amenorrhea, secondary
amenorrhea including undiagnosed pregnancy); anovulation; dysmenorrhea;
endometriosis; hirsutism, virilization; mittelschmerz; pelvic pain; polycystic ovarian
syndrome; postcoital bleeding; premenstrual syndrome
Sexual dysfunction: dyspareunia; orgasmic dysfunction; sexual desire/arousal
syndrome; vaginismus
Traumatic and mechanical disorders: Asherman syndrome; chronic inversion of uterus;
chronic pelvic pain syndrome; cystocele; imperforate hymen; injuries, wounds, and burns
affecting the female reproductive system and injuries, wounds, burns, and blast injuries;
ovarian torsion; pelvic relaxation; prolapse, vaginal walls, uterine, uterovaginal; rectocele;
urethrocele
Congenital disorders: müllerian agenesis; uterus didelphys, bicornuate uterus; short cervix
Adverse effects of drugs on the female reproductive system and breast: antihistamines,
H2-receptor blockers; benzodiazepines; beta-adrenergic blockers; hormone
replacement; opioids; spironolactone; selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors;
tricyclic antidepressants
Male Reproductive System
Normal Processes
Embryonic development, fetal maturation, and neonatal changes, gametogenesis
Organ structure and function
structure, male genitalia and prostate
function, male genitalia and prostate (eg, spermatogenesis, puberty)
intercourse, orgasm, erection
Cell/tissue structure and function, including hypothalamic-pituitary-gonadal axis, sex
steroids, and gestational hormones
Reproductive system defense mechanisms and normal flora
Repair, regeneration, and changes associated with stage of life
Abnormal Processes: Health and Health Maintenance, Screening, Diagnosis,
Management, Risks, Prognosis
Infectious, immunologic, and inflammatory disorders
infectious disorders: balan
Did you try this amazing source for the latest practice tests?
I am thrilled to announce that I passed my USMLE certification exam with flying colors, and I could not have done it without the help of Killexams.com. Their questions and answers were invaluable in preparing me for the exam, and I am so grateful to have had access to their resources. The questions on the exam were similar to those provided by Killexams.com, which helped me to feel confident and well-prepared. Now that I am USMLE certified, I am excited about the new opportunities that await me.
Actual USMLE exam questions to help you pass on the first attempt.
If you are in need of high-quality USMLE practice tests, look no further than killexams.com. Their test preparation is superb and highly effective, helping me to achieve a high score on the exam. I was initially skeptical of the value of USMLE practice tests, but killexams.com proved me wrong with their excellent material. Join killexams.com without fear if you are seeking top-notch exam preparation material.
Make a quick and smart move: read these USMLE questions and answers.
My first experience with Killexams.com for the USMLE exam exceeded all expectations. Their practice tests were not only valid but also of exceptional quality, with real exam questions that prepared me thoroughly. The exam simulator was reliable, and the overall experience was impressive. I wholeheartedly recommend Killexams.com to colleagues and aspiring candidates.
Can I find real exam questions and answers for the updated USMLE exam?
Failing the USMLE exam shattered my confidence, but thanks to Killexams.com, I scored 87% and passed the exam. The subjects in USMLE were difficult for me, and I almost gave up on taking the exam again. But my friend recommended Killexams.com questions and answers, and within four weeks, I was completely ready for the exam.
No time to study USMLE course books! I need something quick to prepare.
I achieved a score of 92% on the USMLE exam today, with Killexams.com being my primary source of preparation. For those intending to take the exam, I highly recommend utilizing the resources provided by Killexams.com. The information is relevant, and the questions are accurate. I am extremely satisfied with my experience on this website, and I plan on returning for all my future USMLE certification exams.

| PDF Questions and Answers | : 849 (Complete Set) |
| File Format | |
| Premium Files Update | : May 30, 2025 |
| Files Delivery | : Instant (5 to 10 min.) |
| Compatibility | : All Desktop and Mobile Devices |
| Delivery Method | : Download Account |
| Sample Download | : USMLE Exam PDF |

|
Killexams now introduces Online Test Engine which works on iPhone, iPad, Android, Windows and Mac. USMLE Online Testing and Learning facility will help you prepare your test on any device. Our OTE provide all features to help you memorize and practice test questions and answers. It is best to Practice USMLE Exam Questions so that you can answer all the questions asked in test center. Our Test Engine uses Questions and Answers from Actual United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam.
| Desktop Test Engine Questions | : 849 |
| Software Version | : 3.0.9 |
| Access | : Unlimited |
| File Type | : VCE, sis |
| Access Activation | : Instant (5 to 10 min.) |
| Support OS | : Windows (All Versions) |
| Delivery Method | : Username/Password | Software Demo | : Demo Software Download |
| Installation Guide | : Video Guide |

|
Killexams Exam Simulator 3.0.9 is industry leading Test Preparation Software for USMLE exam. We Guarantee that when you Practice USMLE Exam with our VCE Exam Simulator, you will be confident in all the topics of the exam and will be ready to take the actual test any time. Our Exam Simulator contains Questions and Answers from real United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam.
Choosing the right resource for certification preparation can be challenging, as candidates seek reliable, high-quality materials to ensure success. Killexams.com is dedicated to providing top-tier practice tests, meticulously updated to maintain accuracy and relevance. Our commitment to excellence has earned the trust of countless satisfied candidates who have successfully passed their exams with ease and confidence. At Killexams.com, we prioritize quality, credibility, and customer satisfaction, ensuring our practice tests, PDF questions, and exam simulators are designed to deliver exceptional value. We stand by our reputation, built on consistent positive feedback and proven results. Be cautious of misleading claims from competitors attempting to undermine our trusted service. With thousands of successful candidates and a robust suite of preparation tools, Killexams.com is your dependable partner for certification success. Explore our sample questions and exam simulators to experience why we are recognized as a leading provider of certification practice tests.
Is Killexams.com Legit?
Yes, Killexams is fully legit in addition to fully trustworthy. There are several includes that makes killexams.com real and legitimized. It provides knowledgeable and fully valid exam questions filled with real exams questions and answers. Price is minimal as compared to a lot of the services online. The questions and answers are up to date on common basis using most recent testprep. Killexams account method and item delivery is extremely fast. File downloading can be unlimited as well as fast. Guidance is avaiable via Livechat and Message. These are the features that makes killexams.com a sturdy website that come with practice tests with real exams questions.
Are killexams Practice Tests Reliable?
Simple answer is YES. There are several Questions and Answers provider in the market claiming that they provide Actual Exam Questions, Braindumps, Practice Tests, Study Guides, cheat sheet and many other names, but most of them are re-sellers that do not update their contents frequently. Killexams.com is best website of Year 2025 that understands the issue candidates face when they spend their time studying obsolete contents taken from free pdf download sites or reseller sites. Thats why killexams.com update Exam Questions and Answers with the same frequency as they are updated in Real Test. Practice Tests provided by killexams.com are Reliable, Up-to-date and validated by Certified Professionals. They maintain Question Bank of valid Questions that is kept up-to-date by checking update on daily basis.
If you want to Pass your Exam Fast with improvement in your knowledge about latest course contents and topics of new syllabus, We recommend to Download PDF Exam Questions from killexams.com and get ready for actual exam. When you feel that you should register for Premium Version, Just choose visit killexams.com and register, you will receive your Username/Password in your Email within 5 to 10 minutes. All the future updates and changes in Questions and Answers will be provided in your Download Account. You can download Premium PDF files as many times as you want, There is no limit.
Killexams.com has provided VCE Practice Test Software to Practice your Exam by Taking Test Frequently. It asks the Real Exam Questions and Marks Your Progress. You can take test as many times as you want. There is no limit. It will make your test prep very fast and effective. When you start getting 100% Marks with complete Pool of Questions, you will be ready to take Actual Test. Go register for Test in Test Center and Enjoy your Success.
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 study help
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 answers
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Free PDF
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam guide
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 guide
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 information hunger
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 USMLE+learning
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 answers
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 test prep
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam guide
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam contents
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 study help
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 official questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam contents
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 PDF Download
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 study help
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Free PDF
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam cram
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 USMLE+learning
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam contents
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 boot camp
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Latest Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam syllabus
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 education
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 certification
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 PDF Download
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 course outline
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Practice Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 USMLE+learning
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam success
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam guide
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 PDF Download
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Question Bank
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Cram
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 test prep
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 techniques
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Latest Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 exam contents
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Real Exam Questions
USMLE - United States Medical Licensing Examination Step 1 Exam Questions
CPUX-F practice questions | NCIDQ-IDFX pdf download | AACN-CMC test prep questions | Servicenow-CIS-CSM assessment test sample | DCDEP practice exam | CWM_LEVEL_II sample questions | CEDS free pdf download | ASDEV01 Study Guide | ISA-IEC-62443 prep questions | GPHR exam tips | AMWA-MWC certification sample | API-580 PDF Questions | SC-900 test exam | C1000-176 past exams | SC-401 test practice | CNN boot camp | RNC-OB examcollection | CWOCN exam test | SC-100 study guide | SHRM-SCP practice test |
http://killexams-braindumps.blogspot.com/2020/06/exactly-same-usmle-practice-test-that-i.html
https://killexams-posting.dropmark.com/817438/23697254
https://www.instapaper.com/read/1322507468
https://killexams-posting.dropmark.com/817438/23792529
https://files.fm/f/6qvhpnfc
https://sites.google.com/view/killexams-usmle-exam-dumps
https://www.coursehero.com/file/72154106/United-States-Medical-Licensing-Examination-USMLEpdf/
https://youtu.be/0hf0T-qQEV0
http://feeds.feedburner.com/FreePass4sure9a0-182QuestionBank
Similar Websites :
iPass4sure Certification Questions
Pass4Sure Exam Questions